
Alpes-Maritimes, a bit of regional history
Part 2: the country is in Savoy
(Piedmont Sardinia) from 1388 to 1860
The new "county" of Nice, Savoie,
challenges of European powers during the Renaissance
During the Renaissance, Savoy, and therefore the county of Nice, were victims of the war between François 1st and Charles V between 1504 and 1544.
1524 : Charles Quint invades Provence, subdues the east including Nice. François 1er takes over Nice, the plunder, but is defeated in Pavia in 1525.

1536 : François 1er occupies most of the States of Savoy and Turin, but fails further west. Only Nice " the very faithful »Remains in Savoy. Duke Charles III comes there fold back.
1538 : negotiations initiated by Pope Paul III between Francis I and Charles V lead to peace precarious after the latter invaded Provence again.
Then François 1st allies with Suleiman the Magnificent , against Charles Quint.
1542 : François 1er, looted the villages of Vésubie and Tinée, obtains the surrender of Coaraze, Bonson, Gilette and Tourette-Revest.
1543 : even allied with the Ottomans, its troops on land and its allies by sea (Soliman's fleet with Barbarossa), fail to take Nice. They fall back in September.

Creation of the County of Nice in 1526, belonging to Savoy
1526 : the " New lands of Provence become the " County of Nice »In the administrative (and not feudal) sense only, with four vigueries : Nice, Sospel (including Vintimille and Val de Lantosque), Barcelonette and Puget-Théniers.
Savoy strengthens the fortifications of Nice.
The abuses of the Companies in the 14th and 15th centuries depopulated some parishes. Savoy repopulated some between 1460 and 1520, by appealing to the Ligurians and the Piedmontese.
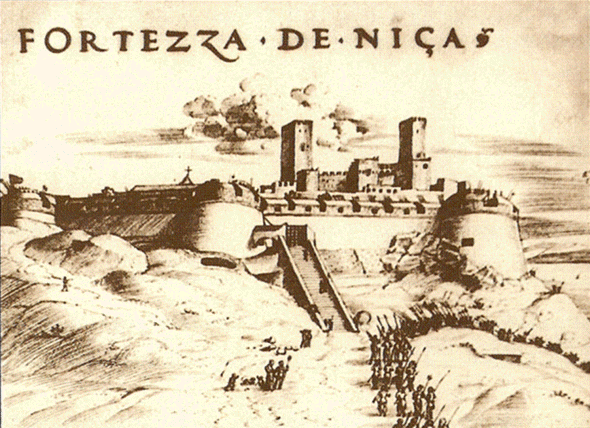

François 1er attack Nice
1559 : by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis, Duke Emmanuel-Philibert found Savoy, Piedmont, Bugey and Bresse. and also married the sister of King Henry II, daughter of François 1st.
This important treaty between France on one side and Spain and the Holy Roman Empire on the other put an end to French interference in Italy. Its agreements remain in force for more than a century and mark the beginning of Spanish predominance in Europe.
Savoy underwent French occupation for 23 years (1536 to 1559) but reaped the benefits of positive reforms.
She strengthens Nice, the surrounding towns, installs forts in eastern Provence. The county of Tende is attached to that of Nice.
During this time, the kingdom of France improves the defenses of western Provence.
Confrontations and alliances in the 17th and 18th centuries,
the Duchy of Savoy becomes Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia
The Protestant reform affects Provence but little the county of Nice.
Wars of religion affect cruelly the French West of Provence. Savoy is participating in it.
1589 : at the beginning of the reign of Henri IV, the Ligueurs (these Catholics already strongly opposed to the Protestant "heresy", became so powerful that they threaten the king) form two clans, the Carcists (French named after the Comte de Carcès) and the Savoyards.
TO the west, French Provence was besieged by the Ligueurs, especially in Grasse where the city chose Henri IV against the League.
To complete the conquest of Provence, the Ligueurs ask the Duke of Savoy for help after the death in front of Grasse of the local Ligueur chief favorable to their clan, Hubert de Garde de Vins. Savoy in 1590 therefore occupies Antibes, Saint-Paul, Grasse, Cannes and Aix.
1591 : the Savoyards are rejected and the County of Nice is invaded by the French anti-League from the north, but their progress is stopped.
Then Henri IV abjures the Protestant faith in 1593 and appoints the Duke of Guise, notorious Ligueur governor of Provence. The Duke of Savoy then retired.
1600 : after the appeasement of the Edict of Nantes in 1598, Henri IV invaded Savoy, and had the County of Nice occupied by the Duke of Guise, not without resistance.


Savoie and France join forces ; the county of Nice remains in Savoie
1630 : after the death of Charles-Emmanuel, his son Victor-Amédée 1st signs a treaty of alliance, the Treaty of Cherasco with France. This treaty also concludes a local conflict for the succession of the Duchy of Mantua between France and Habsburg-Spain on the sidelines of the Thirty Years War.
There began to emerge a talented and cunning young diplomat, the future Cardinal Mazarin , who acted to promote himself to Richelieu.
1637 : the Savoie-France link is strengthened after the death of Victor-Amédée 1st : his wife, Christine de France , daughter of Henri IV , becomes regent.
The Spanish fleet attacks the garrisons of Sainte-Marguerite and Saint-Honorat. Corn the French retake the Lérins Islands.
Alliances are moving : the lord of Monaco allied with France and thereby got rid of his Spanish protectorate in 1641.
1642 : the Spanish are driven out of Nice but Victor-Amédée II , on the other hand, wanted to move away from French supervision.

But nothing stands still.
After a new French attack, the Duchy of Savoy becomes kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia and opposes France (1705 to 1790).
The war resumes soon after on the occasion of the succession of Spain . Victor-Amédée II (known as "the Savoy fox") is first of all allied to Louis XIV, then does an about-face in favor of the emperor.
1706 : French troops take Nice in January. The county is occupied until Sospel, except the Roya valley defended by the Fort de Saorge.
Nice changes function and loses its military role.
1707 : the Duke of Savoy recaptures Nice, plunder and massacre in the west, was arrested in Toulon, then beats a retreat before the resumed French assault the county of Nice to Sospel.
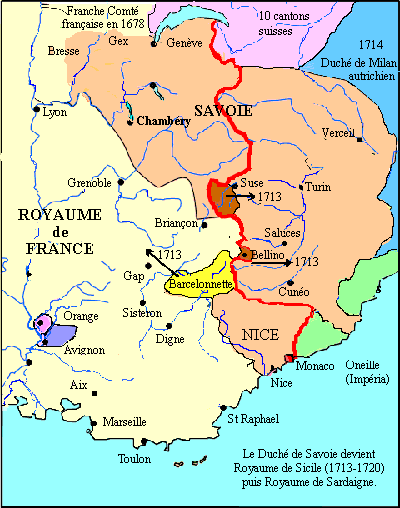
1713 : the Treaty of Utrecht returns all its territories to the duchy but concedes Barcelonette to the French. Victor-Amédée finally obtains the Sicily that he will exchange for the kingdom of sardinia in 1720 .
1720 : the duchy becomes kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia.



Recording of the Edict of Nantes in 1598

Huguenot massacre in Orange in 1560 and St-Barthélémy in Paris in 1572

1601 : finally, Henri IV recognizes in Savoy the marquisate of Saluces and obtains in exchange Bresse, Bugey and the country of Gex.
At the initiative of Charles Emmanuel 1st of Savoy, this period is also marked in 1610 , by the construction of the route of the Route Royale Nice-Turin in particular for the salt trade from Hyères to Turin , through the creation of Harbor franc in 1612. Baroque architecture develops and a sovereign court, the Senate of Nice , was created in 1614 .
1621 : under the Savoyard regime, the County of Nice becomes a city of lawyers. But its governor, Annibal Grimaldi count of Beuil betrays Savoy : condemned, he and executed.
1629 : a matter of succession is a pretext for a new war between France and Savoy; the latter is invaded. The peace signed in 1631 allows Spaniards who came to help Savoy in the region to stay there 12 years.

Victor-Amédée 1st tired; and the agile gaze, insightful and confident of Mazarin

Savoy attacked then restored under French alliance (1691 to 1696)
Of 1688 To 1713 : war resumes between France and Savoy.
1690 : Victor-Amédée II allies with the emperor and the king of spain versus Louis XIV as part of the Augsburg League . The French then occupied Savoy.
1691 : the County of Nice ends up being totally occupied by the French.
Louis XIV, then at war against Europe united since 1689 (the League of Augsburg), tries in this maneuver of which the Duke of Savoy is the object, to unbalance the League by making the Duke his ally. The Duke is no longer supported by his neighbors in the League. Nor is it able to withstand the French steamroller.
1696 : by the Treaty of Turin, Louis XIV returns all his conquests to Victor Amédée II, who, in return must marry her daughter with the Duke of Burgundy, grandson of Louis XIV. Victor Amédée will therefore be the grandfather of the future Louis XV.
1697 : the maneuver will succeed since the Treaty of Ryswick will conclude the end of the League war.

1730 : after abdication volunteer of Victor-Amédée II in favor of his son Charles-Emmanuel III, the latter pursues a policy of alliance against France.
During the Austrian succession, Gallispans (Franco-Spanish troops) and Austro-Piedmontese clash between 1744 and 1749. The war affected the hinterland of Nice , since the city lost its military role.
1749 : the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle returns the County of Nice to Piedmont.
In Nice, the population resumes its development and extends outside the old ramparts, going from 14 600 inhabitants in 1718 To 20 000 in 1790 . The elites of Nice are attracted to Turin. E girls are doing their studies and careers in the administration, the army, diplomacy.
At the same time, English aristocrats choose Nice as a winter resort. So the of Duke of York , brother of the king George III , in 1764 . In the years 1780 , the winterers numbered around 300.
The King of Piedmont consolidated the County of Nice, organized education, created other infrastructures, made the road from Nice to Turin suitable for vehicles in 1788.
Nice is expanding and becoming more beautiful. The border between the county and France is slightly modified. Sospel becomes the 2nd city of the county.
The beginnings of Italian unification
Creation of the Alpes-Maritimes department in 1793 (except eastern fringe)
1790 : a new division after the Revolution inserts the region of Grasse in the department of Var.
1792 : after France entered the war against Austria and Prussia, Nice was taken without fighting, in September. Then elections are won by the party in favor of the meeting of the County of Nice to France. What the Convention endorses the January 31 1793 .
1793 : the Alpes-Maritimes department, the first of the name, was created in February except for the current eastern fringe.
The high valleys of Tinée, Vésubie and Roya remain Piedmontese. In June 1793, the French general Brunet was defeated at Authion.
In the hinterland, barbets (between political struggle and brigandage) oppose the French troops.
1794 : in April, Masséna takes over Saorge and Tende. But by the Treaty of Paris in 1796, the King of Piedmont-Sardinia renounced the County of Nice, which disorients opponents of the Revolution .


Napoleon unrolls, loses and takes over the county, adds San Remo and Genoa to his hunting table for the time being
After the coup d'etat of 18 brumaire and the establishment of Consulate , the Austro-Sardinian troops take Nice, then taken over by the General Suchet .
Austria reoccupied the county in May 1800, then the department was taken over by France in June.
1805 : the emperor annex the Republic of Genoa (Ligurian). The western part is attached to the Alpes-Maritimes, which includes, in addition to the districts of Nice and Puget-Théniers, that of San Remo.
With the pursuit in other areas of Napoleonic wars , local public opinion turned away from France.
1813 : the crowd cheers Victor Emmanuel 1st .
1814 : after the fall of Napoleon I , the county of Nice, Piedmont and Savoy returned to Victor-Emmanuel 1st and France renounces the department by first treaty of Paris (May 1814). The old administrative regime and the Italian language are restored.
1815 : after the Hundred Days and Waterloo, the 2nd Treaty of Paris (November) confirms the first. Piedmont-Sardinia also receives the former Republic of Genoa and the protectorate of Monaco (previously French).

The return of peace and stability are appreciated in Nice which, under Piedmontese mandate, continues to develop.
British winter visitors come more in number to Nice and its holiday region.
Cannes also become city of winter and aristocratic residence, counted 25 British families in 1843 ; a little thanks to (or because of) the cholera epidemic for which the cordon sanitaire between France and the county is holding Lord Brougham in Cannes.
1847 : Menton and Roquebrune are annexed by Piedmont-Sardinia after Monegasque unrest.
1848 : Nice benefits from the political liberalization movement launched by Charles-Albert in 1847 . the Statuto is promulgated on March 4 . The House of Representatives is now elected to censal suffrage . The elected members of Nice are all liberals.
At the same time, Giuseppe Garibaldi, born in Nice, starts to get famous.
The Jewish ghetto of Nice (the Giudaria) created in 1430 is suppressed; it is given to Jews the same rights as Catholics.
Victor Emmanuel 1st implements the policy of " good government (Buon Governo).
Nice regains its Senate . Teaching is reorganized with Jesuits , the Brothers of the Christian schools , the creation of schools of right of medicine and surgery .
the diocese of Nice is detached from the Aix province and depends on the archdiocese from Genoa.
Nice is experiencing a period of stability political and is won by liberal ideas .
Its population increases sharply by 23 500 inhabitants in 1815 to 44 000 inhabitants in 1858 .


Victor Emmanuel 1er and Garibaldi photographed by Nadar in 1870
Period changes
1860, Definitive return of Nice and its region to France

In the weekly "Le Monde Illustré" of March 31, 1860, reception in Paris of a delegation from Savoy by Napoleon III at the Tuileries
1860 : after the Plombières agreements between Napoleon III and Cavour , the Turin Treaty of 24 mars ratifies these changes.
In Nice, the population, reluctant, ends up accepting when the king Victor Emmanuel II , the April 1 , solemnly asks him, in the name of the effort in favor of Italian unity.
a plebiscite covering the county of Nice but also Menton and Roquebrune, universal male suffrage is organized in April 1860 . The opponents of annexation abstain. The plebiscite wins 83 % of " Yes »Throughout the County of Nice.
Garibaldi from Turin protests against irregularities.
The department of Alpes-Maritimes, second of the name, was created on June 23 by the addition of the county of Nice and the district of Grasse detached from the department of Var.
Monaco abandoned its rights to Menton and Roquebrune in February 1861 against compensation.
The districts are those of Nice, Puget-Théniers and Grasse.
Political life in Nice is fairly calm under the Second Empire. On the major infrastructure works are launched in the valleys of Vésubie and Var, the Basse Corniche is open 1862, the bridge over the Var built from 1862 To 1864 . The train arrives in Nice in 1864 and in Menton in 1869 .
French interests and Italian unification : definitive return of the department to France in 1860
1851 : after the coup d'etat of Napoleon III, French republicans take refuge in Nice.
Turin abolished the franchises of the port of Nice in 1853 but developed the infrastructures (roads in the high country, bridges, embankment of the Var).
A "French party" is structured from 1848 around the newspaper "L'Écho des Alpes-Maritimes".
Napoleon III wants to help Italy to unite, with the aim of containing Austria . In exchange of what the emperor claims the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice , which militarily constitute two important strategic regions.

Vote of the people of Nice in 1860

The Kingdom of Sardinia after the Treaty of Turin

The change in sovereignty is not going smoothly.
With the removal of the Court of Appeal , the lawyers of Nice lose their customers.
Numerous aristocrats and other inhabitants , supporters of the House of Savoy , also leave Nice to settle permanently in Italy (1/4 of the population of Nice emigrate to Italy in one decade).
Politically, the Nice liberals and supporters of Garibaldi did not appreciate Napoleonic authoritarianism. Elements of the right (aristocrats) as of the left (Garibaldians) therefore wanted the return from Nice to Italy. Moreover, for Garibaldi, his hometown can only be Italian.
The disputes at the end of the Second Empire express themselves here in the results of plebiscite of May 1870 where Nice is among the rather opposite cities on a diet.